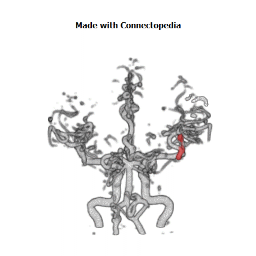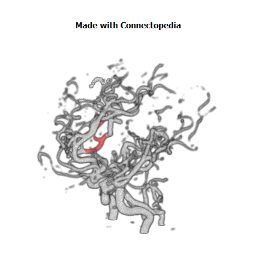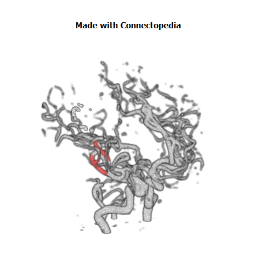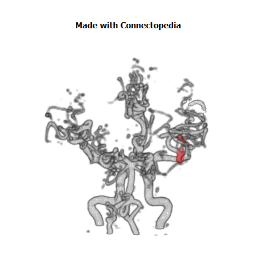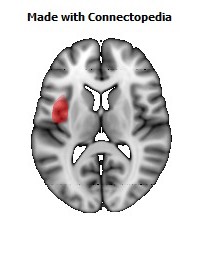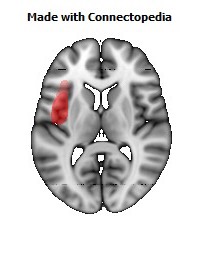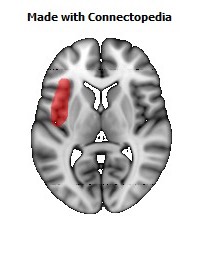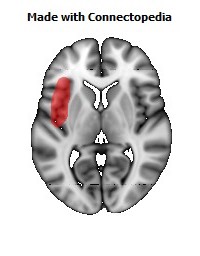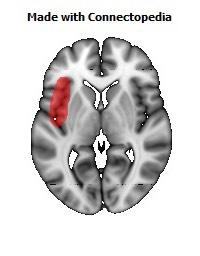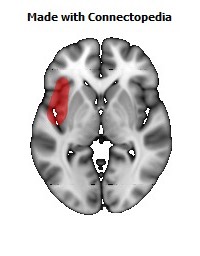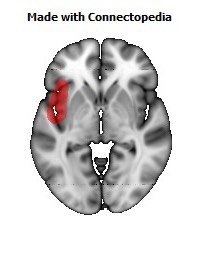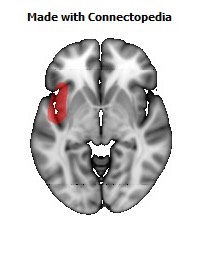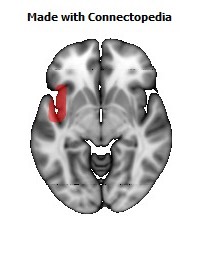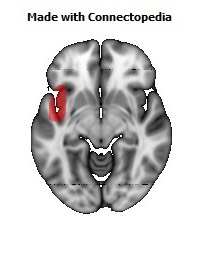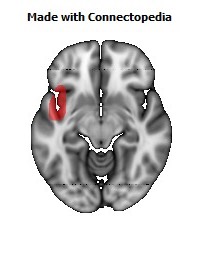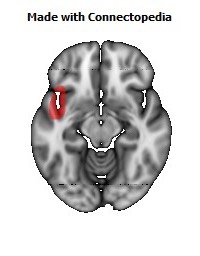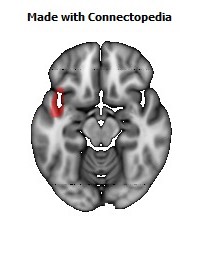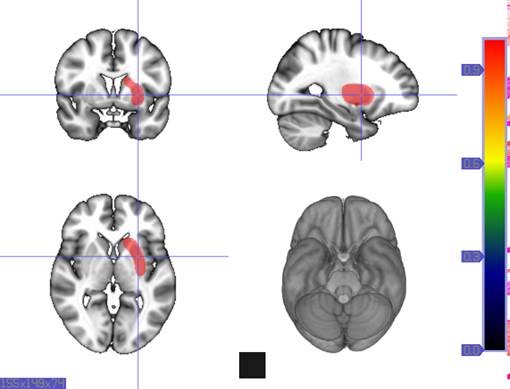
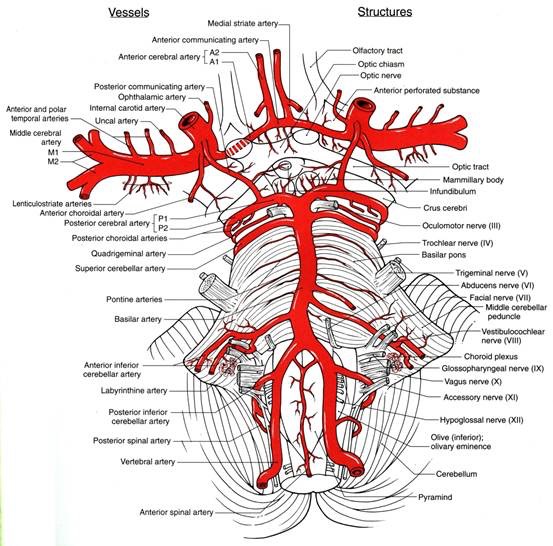
The insula is located at the base of the sylvian fissure and is a potential site for pathological processes such as tumors and vascular malformations. Knowledge of insular anatomy and vascularization is essential to perform accurate microsurgical procedures in this region.
Studied on 20 human cadavers brain, arteries supplying the insula numbered an average of 96 (range 77-112). Their mean diameter measured 0.23 mm (range 0.1-0.8 mm), and the origin of each artery could be traced to the middle cerebral artery (MCA), predominantly the M2 segment. In 22 hemispheres (55%), one to six insular arteries arose from the M1 segment of the MCA and supplied the region of the limen insulae. In an additional 10 hemispheres (25%), one or two insular arteries arose from the M3 segment of the MCA and supplied the region of either the superior or inferior periinsular sulcus. The insular arteries primarily supply the insular cortex, extreme capsule, and, occasionally, the claustrum and external capsule, but not the putamen, globus pallidus, or internal capsule, which are vascularized by the lateral lenticulostriate arteries (LLAs). However, an average of 9.9 (range four-14) insular arteries in each hemisphere, mostly in the posterior insular region, were similar to perforating arteries and some of these supplied the corona radiata. Larger, more prominent insular arteries (insuloopercular arteries) were also observed (an average of 3.5 per hemisphere, range one-seven). These coursed across the surface of the insula and then looped laterally, extending branches to the medial surfaces of the opercula.